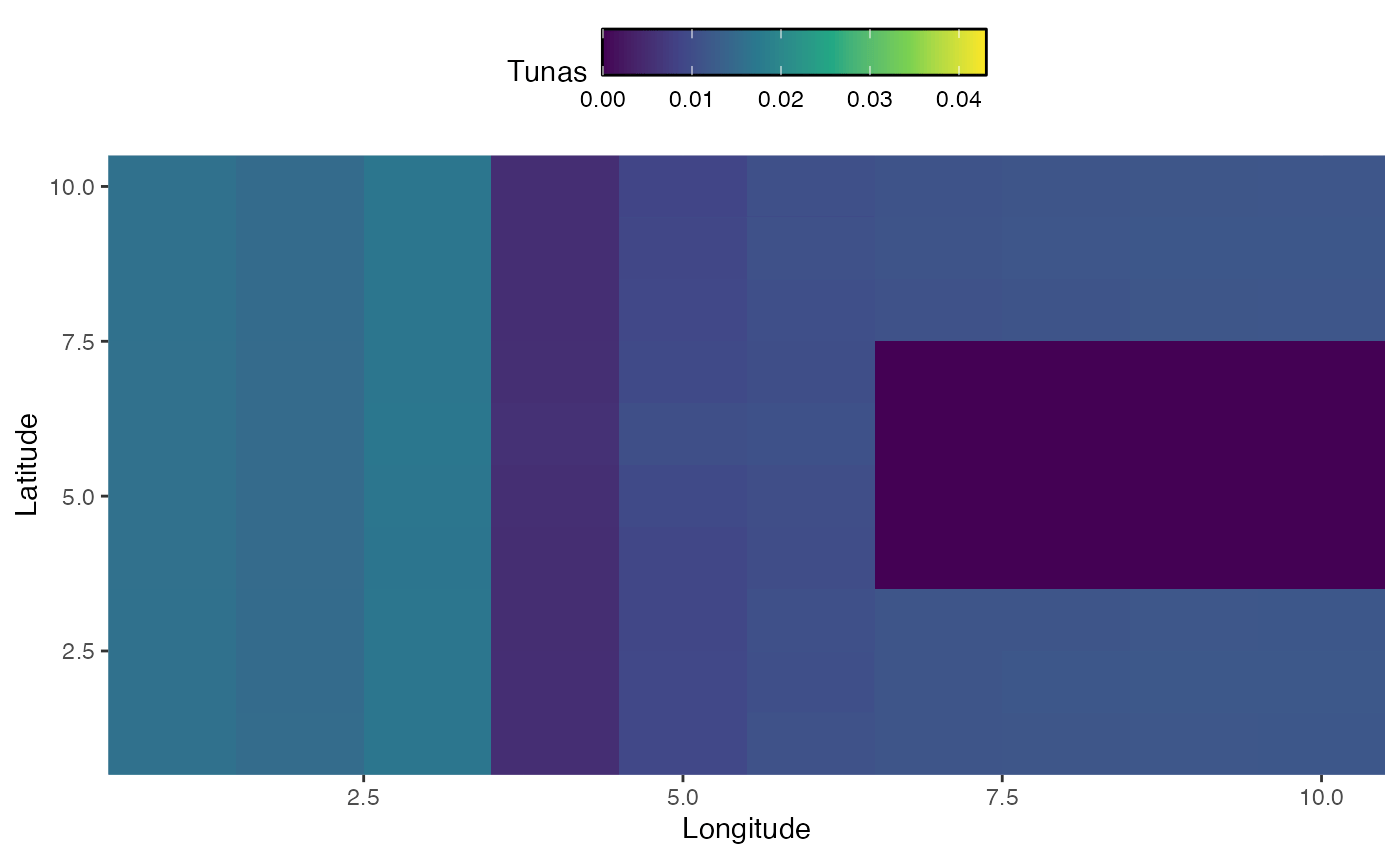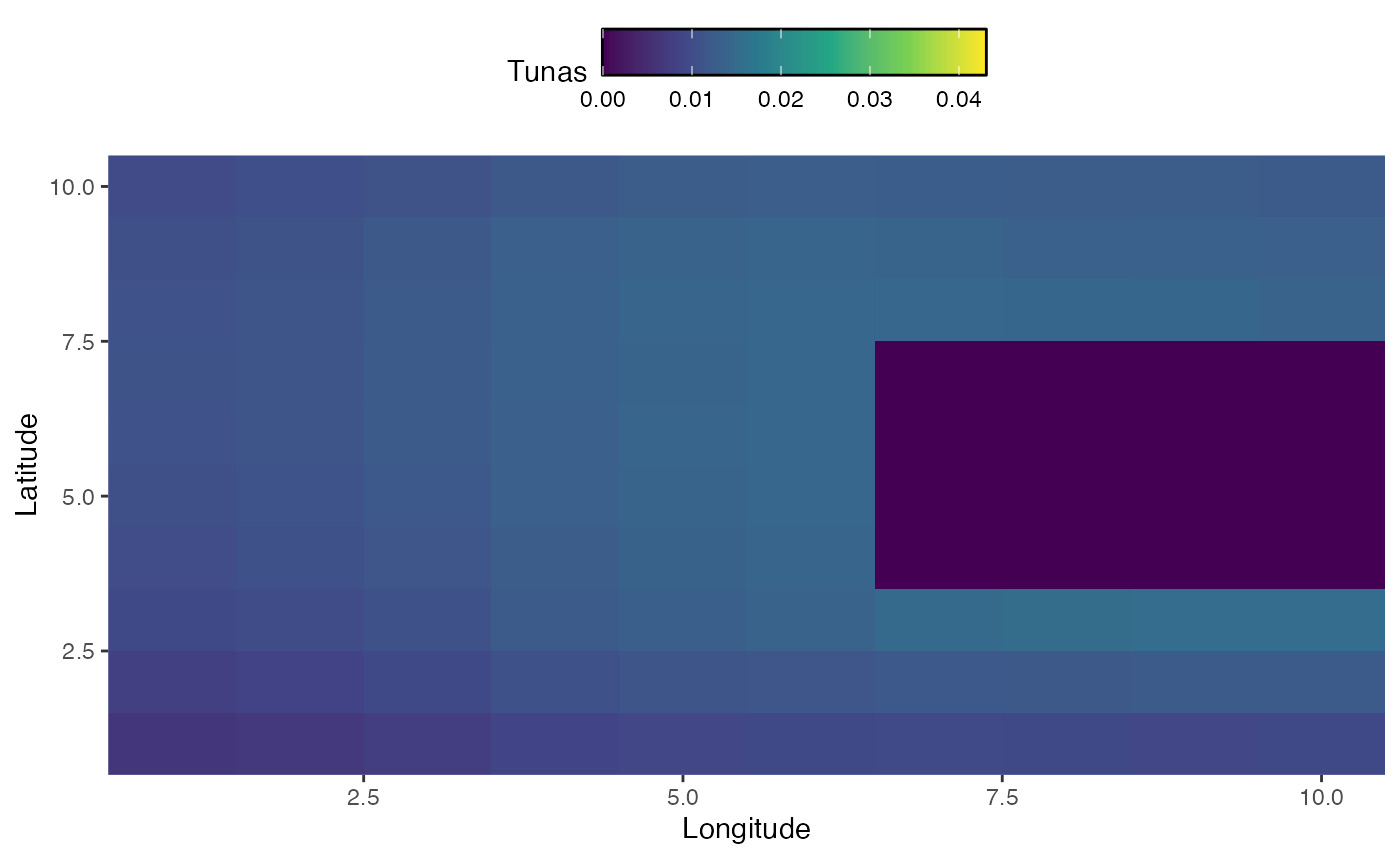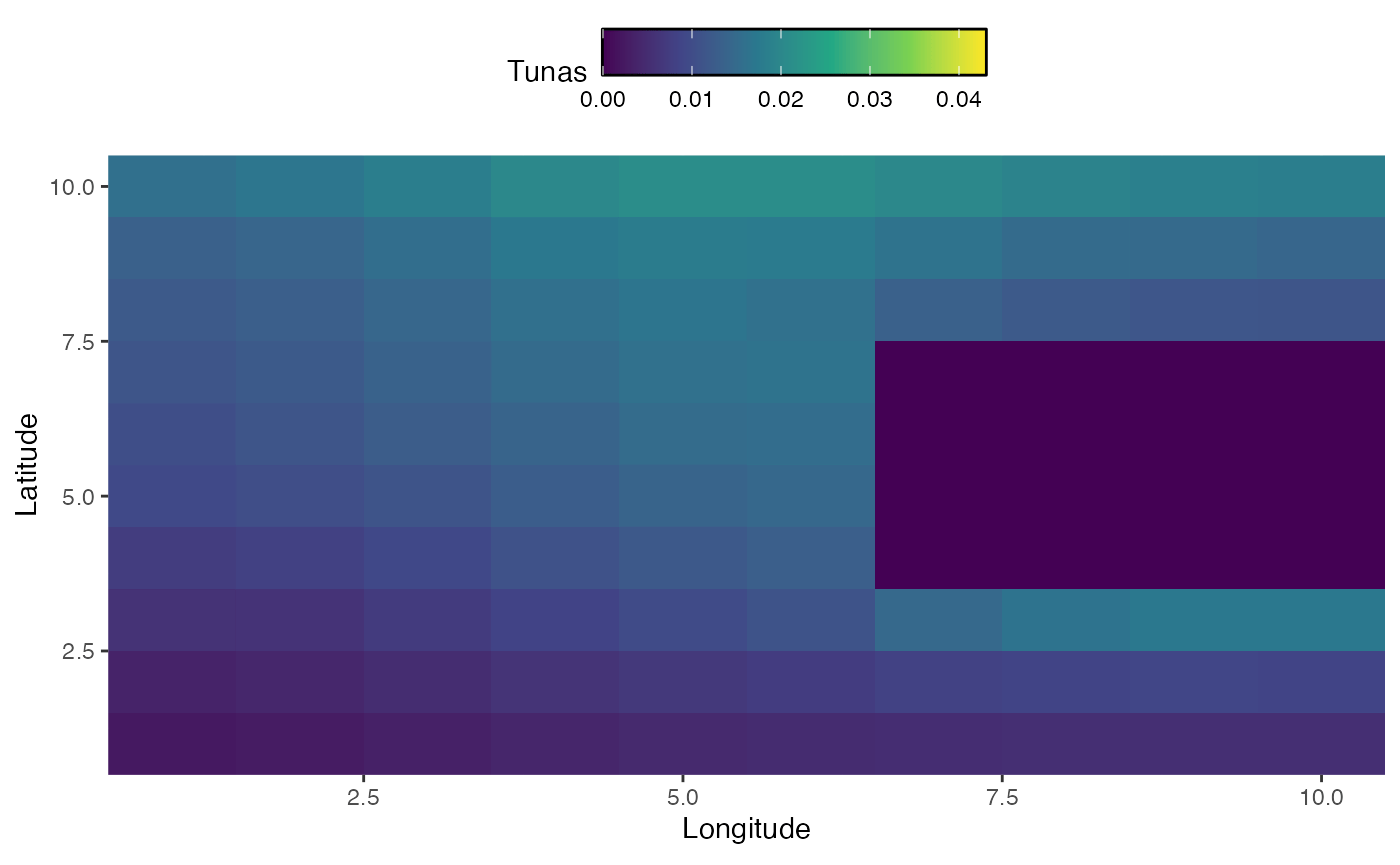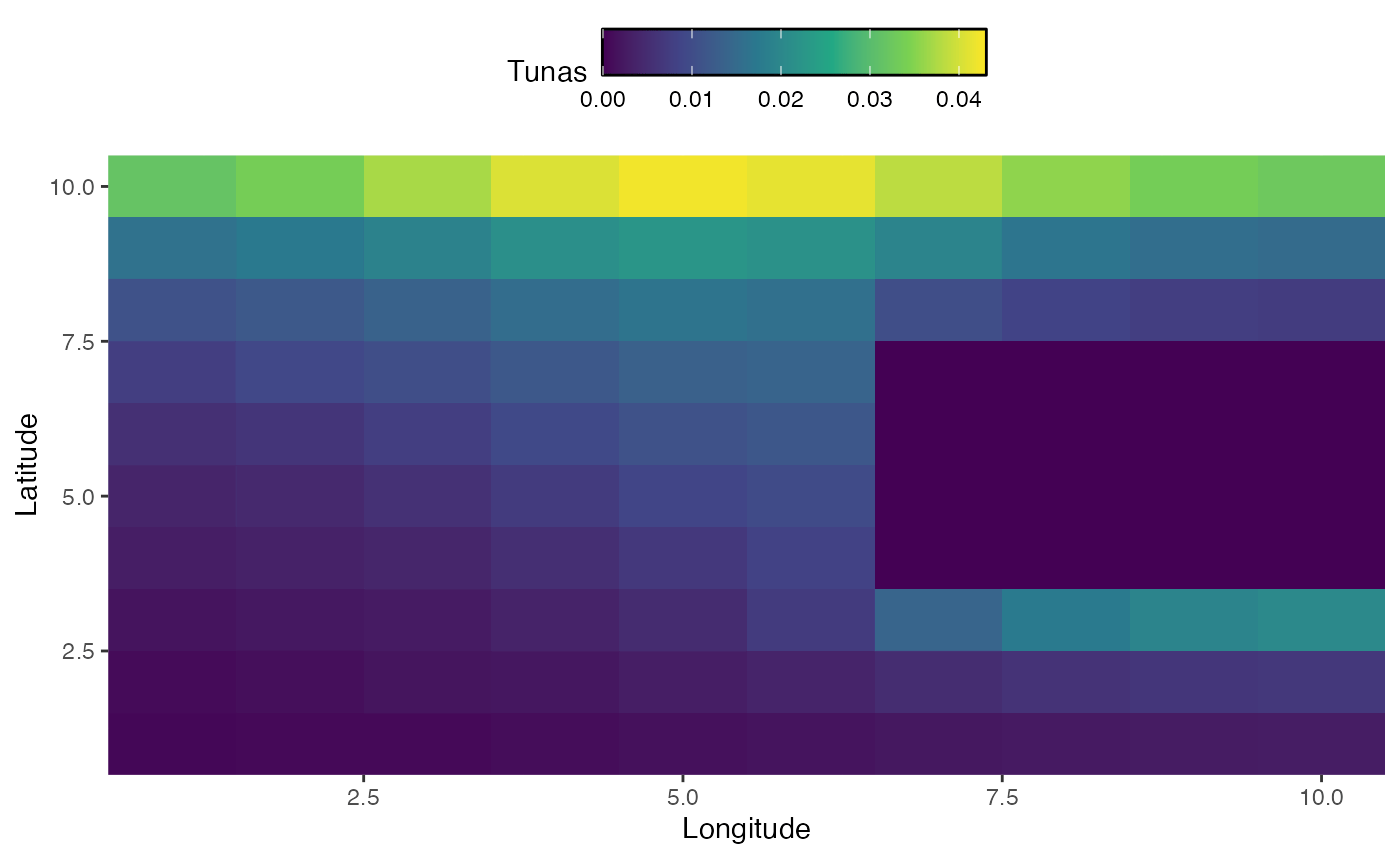Along with allowing users to create simulation where habitat varies in space, or where regulations vary in space, you can also allow for habitat that changes in time, either cyclically or with a trend.
Spawning Aggregations
In this first example, we’ll create a scenario where the year is split up into four seasons. In this simulation, bigeye tuna spend half the season in the far “east” of the domain, and half the season concentrated on a spawning ground where spawning occurs.
As an added twist, you can add landmasses to your model by setting
the habitat value to NA in the patches covered by land.
This is different than setting habitat to 0, as a zero value simply
implies that organisms don’t want to live in that patch, where land
prohibits them from passing over or through those cells.
By default if the length of the habitat vectors is less than the time steps, the model treats the supplied habitat list as being seasonal.
library(marlin)
library(tidyverse)
library(gganimate)
library(ggridges)
library(gifski)
years <- 20
resolution <- 10
seasons <- 4
steps <- years * seasons
time_step <- 1 / seasons
land <- expand_grid(x = 1:resolution, y = 1:resolution) %>%
filter(between(x, 7, 10) & between(y, 4, 7)) %>%
mutate(land = TRUE)
h1 <- expand_grid(x = 1:resolution, y = 1:resolution) %>%
mutate(habitat = dnorm(x, resolution / 2, .02 * resolution) * dnorm(y, resolution / 2, .02 * resolution)) %>%
mutate(habitat = habitat * (x >= 4)) %>%
left_join(land, by = c("x", "y")) %>%
mutate(habitat = ifelse(is.na(land), habitat, NA)) %>%
select(-land)
h2 <- expand_grid(x = 1:resolution, y = 1:resolution) %>%
mutate(habitat = -.5 * x + 10) %>%
mutate(habitat = habitat * (x < 4)) %>%
left_join(land, by = c("x", "y")) %>%
mutate(habitat = ifelse(is.na(land), habitat, NA)) %>%
select(-land)
bigeye_habitat <- h1 %>%
pivot_wider(names_from = x, values_from = habitat) %>%
select(-y) %>%
as.matrix()
# huh <- tidyr::pivot_longer(as.data.frame(bigeye_habitat), tidyr::everything())
#
# h1$habitat2 <- as.numeric(huh$value)
bigeye_habitat2 <- h2 %>%
pivot_wider(names_from = x, values_from = habitat) %>%
select(-y) %>%
as.matrix()
recruit_habitat <- bigeye_habitat
recruit_habitat[!is.na(recruit_habitat)] <- 1
fauna <-
list(
"bigeye" = create_critter(
scientific_name = "thunnus obesus",
habitat = list(bigeye_habitat, bigeye_habitat2),
season_blocks = list(c(1, 2), c(3, 4)),
adult_home_range = c(5, 5), # standard deviation of the number of patches moved by adults
recruit_home_range = 10,
recruit_habitat = recruit_habitat,
density_dependence = "pre_dispersal",
seasons = seasons,
init_explt = 1,
explt_type = "f",
spawning_seasons = c(2, 3),
sigma_rec = 0,
ac_rec = 0,
linf = 100,
vbk = 0.2,
age_mature = 4,
m = 0.2,
weight_a = 1e-4,
weight_b = 3,
max_age = 15,
query_fishlife = FALSE
)
)
fleets <- list(
"longline" = create_fleet(
list("bigeye" = Metier$new(
critter = fauna$bigeye,
price = 10,
sel_form = "logistic",
sel_start = 1,
sel_delta = .01,
catchability = 1e-3,
p_explt = 1
)),
base_effort = 10 * resolution^2,
resolution = resolution
)
)
fleets <- tune_fleets(fauna, fleets)
spawning_ground_sim <- simmar(
fauna = fauna,
fleets = fleets,
years = years
)
processed_spawning_grounds <- process_marlin(sim = spawning_ground_sim, time_step = time_step)
spawning_agg <- processed_spawning_grounds$fauna %>%
filter(age == max(age)) %>%
group_by(step) %>%
mutate(n = n / sum(n)) %>%
ungroup() %>%
ggplot(aes(x, y, fill = n)) +
geom_tile() +
transition_time(step) +
ease_aes("linear") +
scale_fill_viridis_c(name = "Tunas") +
scale_x_continuous(name = "longitude") +
scale_y_continuous(name = "latitude")
dir.create("images", showWarnings = FALSE)
spawning_gif <- gganimate::animate(
spawning_agg,
nframes = 100,
fps = 2,
renderer = gganimate::gifski_renderer()
)
gganimate::anim_save("images/spawning-agg.gif", animation = spawning_gif)
knitr::include_graphics("images/spawning-agg.gif")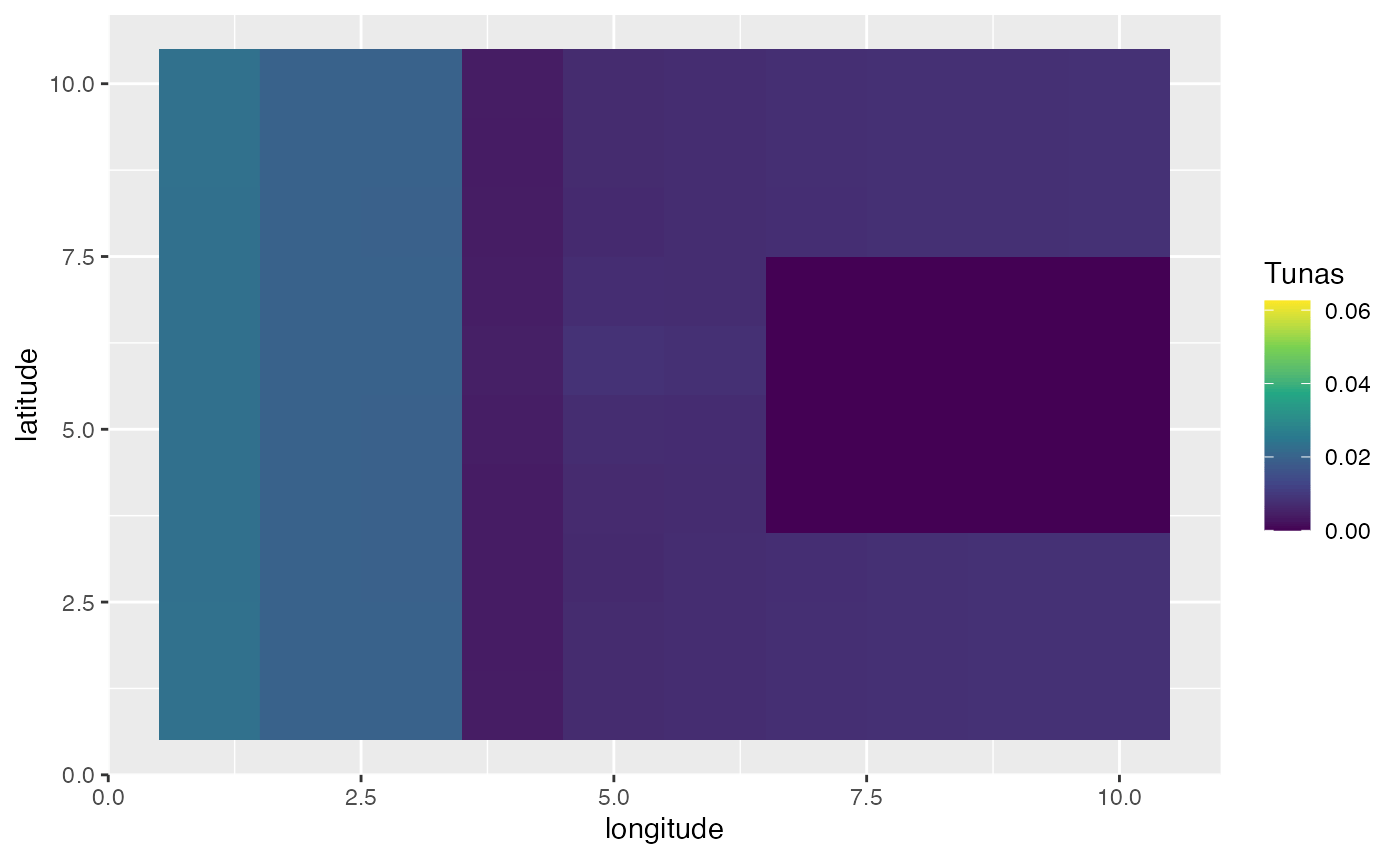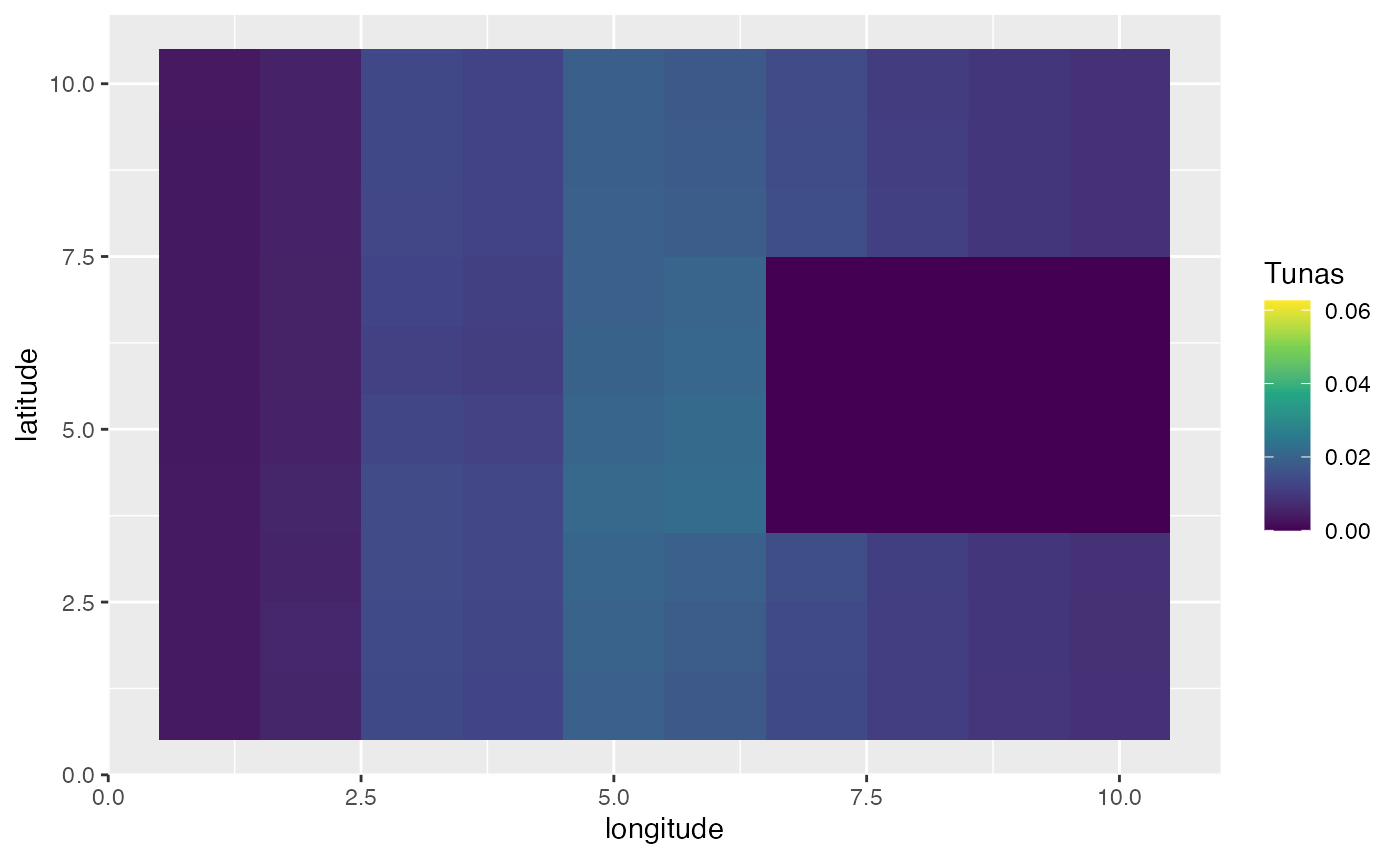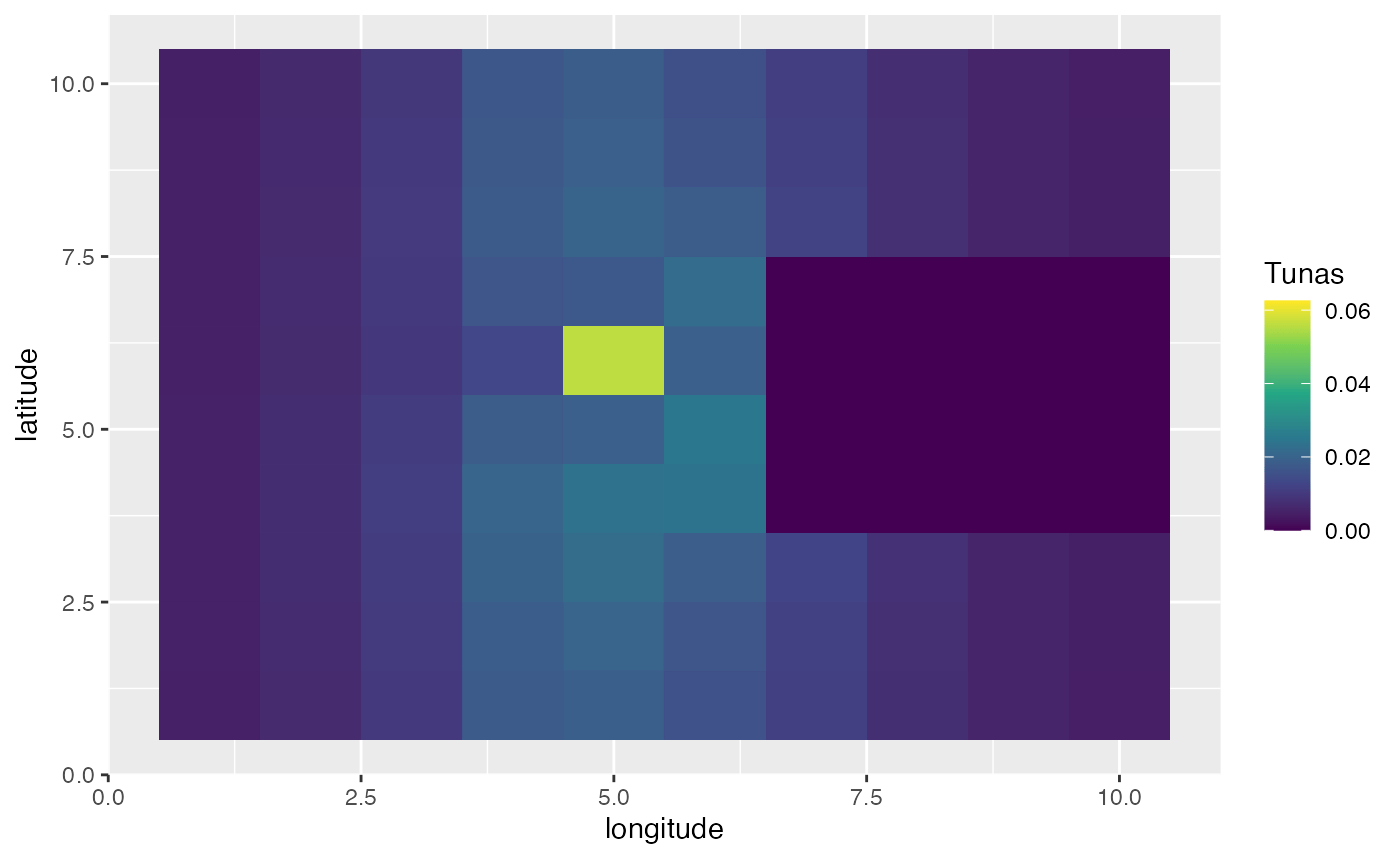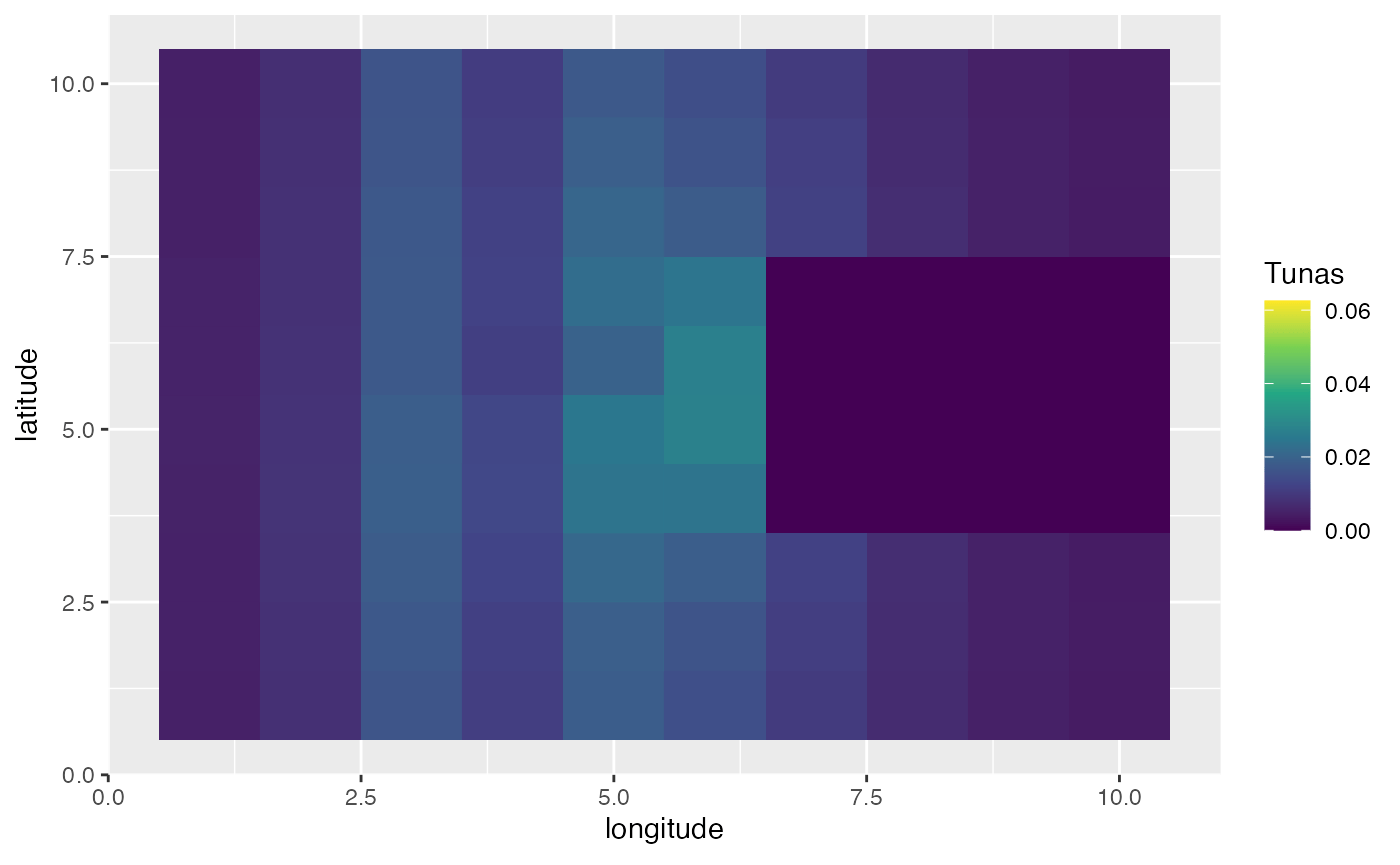
Range Shifts
In addition to seasonal dynamics, we may be interested in active range shifts of species. The mechanics of this work similarly to seasonal dynamics, but require a vectors a vector of habitats equal to either the number of years or the number of steps (where steps is years times seasons per year).
In this case, we sill simulate habitat for bigeye tuna that changes over time, first shifting east and south and then north, while moving around a land mass.
# test habitat vector -----------------------------------------------------
shifting_habitat <- vector(mode = "list", length = years)
for (i in 1:years) {
shifting_habitat[[i]] <- expand_grid(x = 1:resolution, y = 1:resolution) %>%
mutate(habitat = -((y - (1 + i))^2) / 10) %>%
left_join(land, by = c("x", "y")) %>%
mutate(habitat = ifelse(is.na(land), habitat, NA)) %>%
select(-land) %>%
pivot_wider(names_from = x, values_from = habitat) %>%
select(-y) %>%
as.matrix()
}
critter_habitat <- list(bigeye = shifting_habitat)
sim_climate <- simmar(
fauna = fauna,
fleets = fleets,
habitat = critter_habitat,
years = years
)
processed_marlin <- process_marlin(sim = sim_climate, time_step = time_step, keep_age = FALSE)
patches <- expand_grid(x = 1:resolution, y = 1:resolution) |>
mutate(r0 = fauna$bigeye$r0s) |>
left_join(land)
range_shift <- processed_marlin$fauna %>%
group_by(step) %>%
mutate(n = n / sum(n)) %>%
ungroup() %>%
ggplot(aes(x, y, fill = n)) +
geom_tile() +
transition_time(step) +
ease_aes("linear") +
scale_fill_viridis_c(name = "Tunas", guide = guide_colorbar(frame.colour = "black", barwidth = unit(10, "lines"))) +
scale_x_continuous(name = "Longitude", expand = c(0, 0)) +
scale_y_continuous(name = "Latitude", expand = c(0, 0)) +
theme(legend.position = "top")
dir.create("images", showWarnings = FALSE)
range_shift_gif <- gganimate::animate(
range_shift,
nframes = 100,
fps = 4,
renderer = gganimate::gifski_renderer()
)
gganimate::anim_save("images/range-shift.gif", animation = range_shift_gif)
knitr::include_graphics("images/range-shift.gif")